

Pain with pulling on external ear discharge may be present
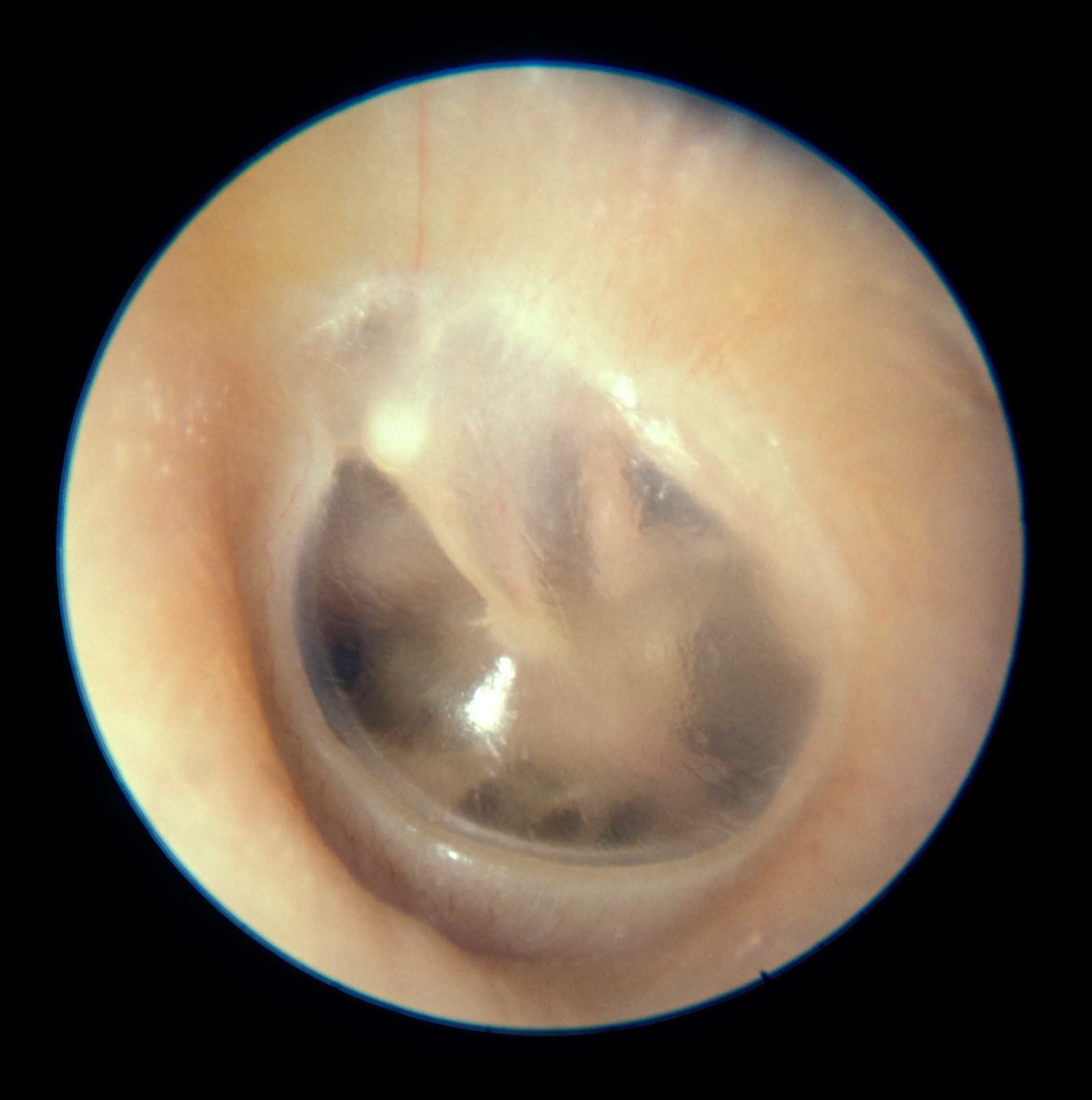
Recent swimming with history of discharge Tympanic membrane retraction or positive tympanographic findingsĪlso associated with aural fullness and intermittent symptoms 7Ĭommonly insects, small toys, peanuts most common in children Prevent with use of topical nasal decongestants or autoinflation Tympanic membrane can show middle ear hemorrhage Pain starts while scuba diving or while flying in an airplane patient may have experienced a recent blast injury 9 Patients with otitis externa typically have pain, redness, swelling, and inflammation along the external auditory canal. A tympanic membrane that has normal color and mobility is not typical for acute otitis media. The tympanic membrane is normally mobile, translucent, and intact. 5, 8 Detection of a middle ear effusion with moderate to severe bulging of the tympanic membrane, new-onset otorrhea not caused by otitis externa, or mild bulging of the tympanic membrane with recent onset of ear pain (less than 48 hours), especially with erythema, is key in the diagnosis of acute otitis media. Specific otoscopic examination findings for the etiology of otalgia are listed in Table 1 5, 7 and Table 2. Physical examination should include inspection of the auricle and periauricular region, as well as an otoscopic examination to visually inspect the tympanic membrane and the external auditory canal. The physician should start the examination by asking the patient to localize the pain, which may reveal a secondary cause (e.g., localization to the temporomandibular joint, myofascial pain localized to the mastoid process). When risk factors for malignancy are present (e.g., smoking, alcohol use, diabetes mellitus, age 50 years or older), computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or otolaryngology consultation may be warranted. Otalgia may be the only presenting symptom in several serious conditions, such as temporal arteritis and malignant neoplasms.
Ear practice exam trial#
History and physical examination usually lead to the underlying cause however, if the diagnosis is not immediately clear, a trial of symptomatic treatment, imaging studies, and consultation may be reasonable options. Primary otalgia is more common in children, whereas secondary otalgia is more common in adults. The most common causes of secondary otalgia include temporomandibular joint syndrome and dental infections. Pain that originates outside the ear is called secondary otalgia, and the etiology can be difficult to establish because of the complex innervation of the ear. Examination of the ear usually reveals abnormal findings in patients with primary otalgia. Pain that originates from the ear is called primary otalgia, and the most common causes are otitis media and otitis externa. Otalgia (ear pain) is a common presentation in the primary care setting with many diverse causes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
